Project Constraints
Primary limitations that will influence the project's design, scope, and execution.
Budget
- Component selection (ESP32 model, microphone, display)
- Overall quality and feature set
- Prototyping costs and potential iterations
Parts & Components
- Availability and shipping lead times
- Ensure parts are high quality
- Hardware compatibility and pin conflicts
Time
- Software development and API integration
- Learning curve for new technologies
- Assembly, testing, and refinement cycles
Coding Ability
- Handling real-time audio streams
- Managing multiple cloud APIs and errors
- Choice of IDE (Arduino vs. ESP-IDF)
Tool Access
- Requires soldering iron, multimeter, etc.
- 3D printer needed for custom enclosure
- Limits physical build quality and ease
Safety
- LiPo battery charging and management
- Proper wiring and short-circuit protection
- Enclosure design for electronic safety
Investigation & Research
Understanding the current landscape of translation devices and related technologies is crucial for making informed design decisions. This research phase explores existing solutions, technical possibilities, and contextual factors that will shape our approach.
Existing Solutions & Case Studies
Select Earbuds
What it does: Real-time translation through earbuds connected to smartphone
Pocketalk Translator
What it does: Dedicated handheld translation device with built-in SIM
Travis Touch Go
What it does: Pocket translator with offline capabilities
M2 Language Translator Earbuds
What it does: Two-way translation earbuds for conversations
DIY ESP32 Voice Projects
What it does: Community projects using ESP32 for voice processing
Inspiration & Technical Exploration
System Architecture Exploration
Based on the research devices, several architectural approaches can be considered. The following are the most promising pathways.
Hardware Architecture Concepts
Concept 1: Minimal ESP32 Design
- Pros: Low cost (~$30), simple assembly
- Cons: No visual feedback, limited user interface
- Use case: Proof of concept, basic functionality testing
Concept 2: Enhanced Display Design
- Pros: Full UI, language selection, status display
- Cons: Higher cost (~$60), more complex assembly
- Use case: Production-ready device with full features
Software Architecture Flow
Translation Process Flow
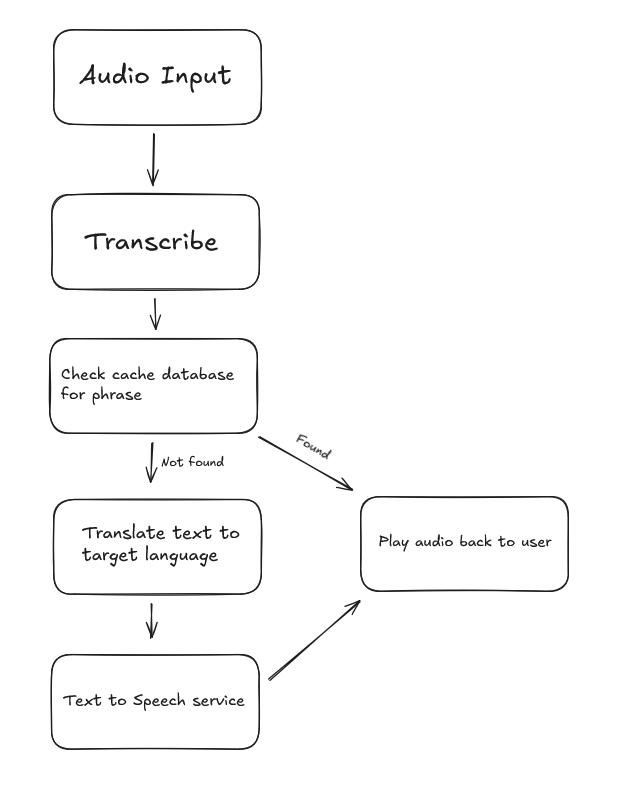
Key Technical Decisions:
- • Use FreeRTOS tasks for parallel processing
- • Implement circular buffer for audio streaming
- • Add retry logic with exponential backoff
- • Cache common phrases to reduce API calls
Visual Design Inspiration & Component Photos
ESP32-S3 Development Board
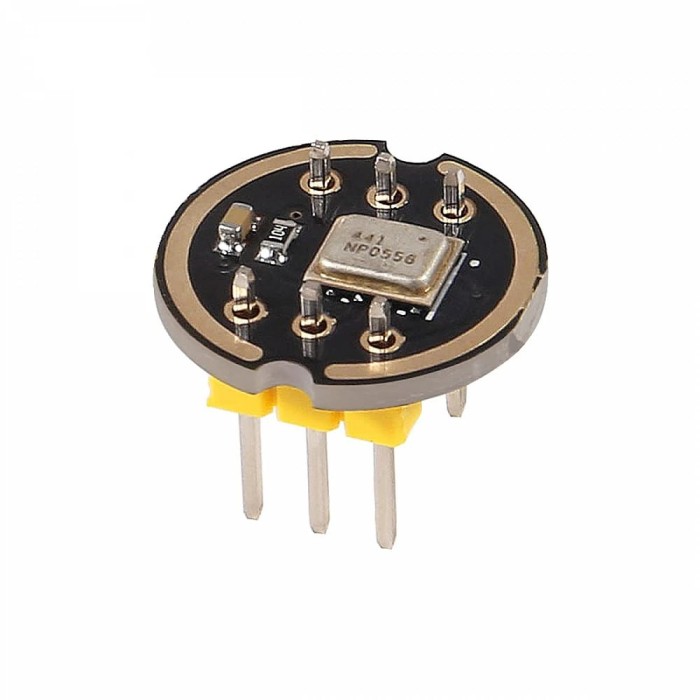

INMP441 I2S Microphone
MAX98357A I2S Amplifier
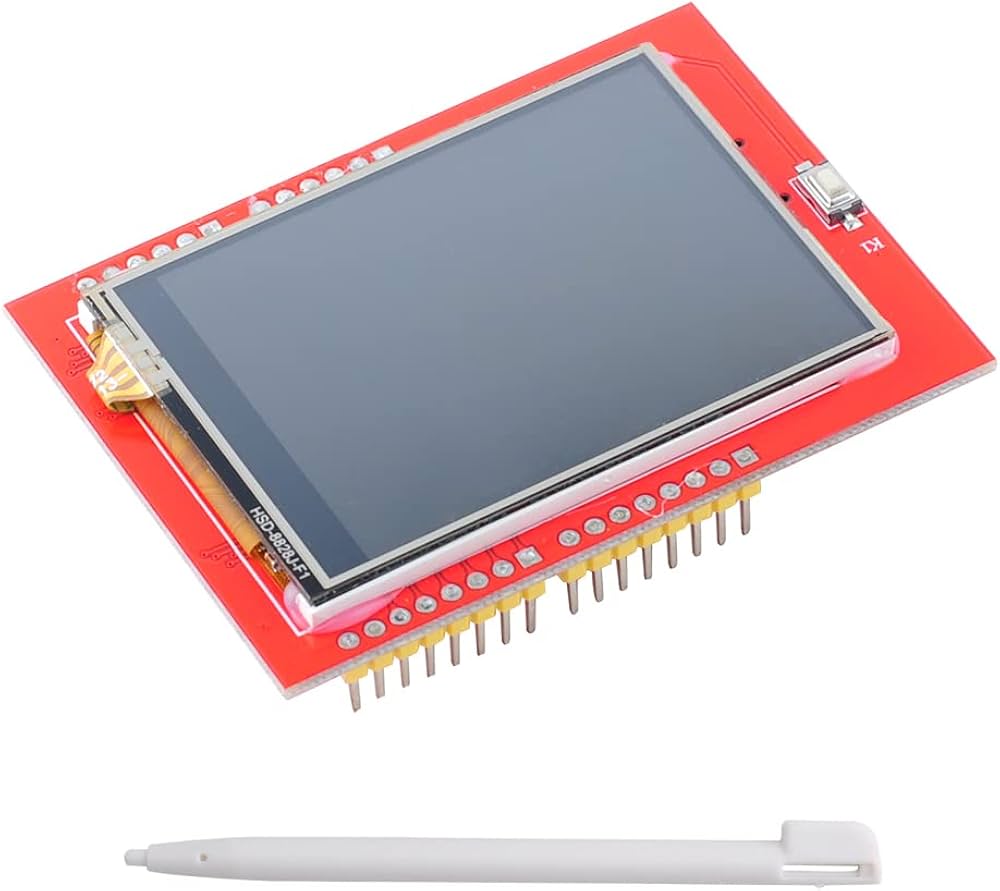

2.4" ILI9341 TFT Display
Touch screen
Rectangular, 120x60x15mm, touchscreen interface

Compact Pod
Compact, 80x80x25mm, button-based interface; Smaller screen
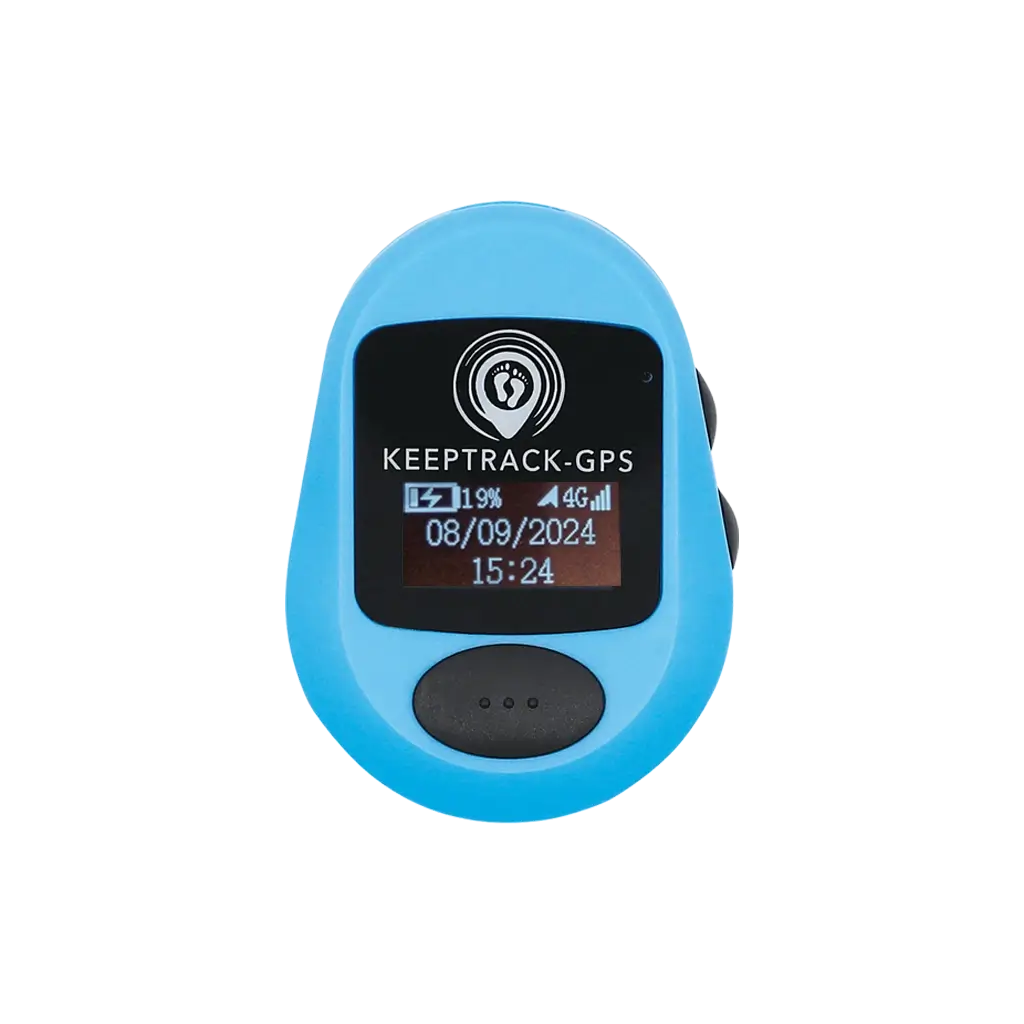

Pendant Style
Wearable, 50x30x20mm, Single Button language switch
The devices shown are third party products.
Development Platform Options
Arduino IDE
Pros: Simple, familiar, good libraries
Cons: Limited debugging, basic audio support
ESP-IDF
Pros: Full control, advanced audio, debugging
Cons: Steeper learning curve, more complex
PlatformIO
Pros: Best of both, VS Code integration
Cons: Additional setup complexity
Visual Studio Code
Pros: Many extensions to assist with coding
Cons: Non-native platform
API Service Comparison
Google Cloud APIs
Accuracy: 95%+ speech, 90%+ translation
Cost: $1.44/hour speech recognition
Azure Cognitive
Accuracy: 93%+ speech, 88%+ translation
Cost: $1.00/hour speech recognition
Amazon Polly/Transcribe
Accuracy: 92%+ speech, 85%+ translation
Cost: $0.96/hour speech recognition
Multiple Providers
Accuracy: Varies
Cost: Typically most cost effective
Assembly Process
Power Consumption Analysis
Whilst these numbers are given from the datasheet, they may not reflect all real world use cases.
Component Power Draw
Battery Life Estimation
Strategy: Have options for sleep modes between translations, display auto-off after 30s, Wi-Fi power saving to maximise power saving when desired by the end user.
Analysis of Findings
Key Design Influences from Research
Hardware Design Decisions
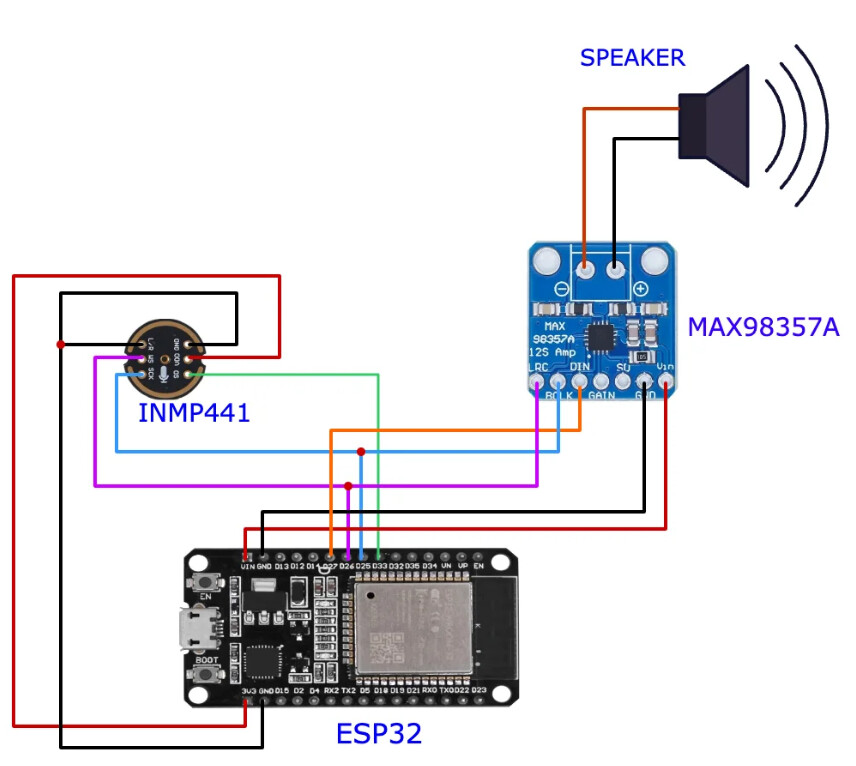
- • I2S Audio Pipeline: INMP441 → ESP32-S3 → MAX98357A will provide professional-grade audio quality similar to high-end commercial devices available on the market.
- • Display Integration: 2.4" TFT allows text display of translations, addressing translation confidence. (showing transcriptions)
- • Standalone Design: No smartphone dependency eliminates connectivity issues, privacy concerns and ease of use
- • Physical Controls: Dedicated push-to-talk button ensures reliable operation under stress
- • Compact Form Factor: Pocket-sized design inspired by successful devices like Pocketalk
Software Architecture Decisions
- • Google Cloud APIs: Primary choice for highest accuracy rates (95%+ speech recognition)
- • Azure Fallback: Redundancy system prevents single-point-of-failure
- • ESP-IDF Platform: Advanced audio handling capabilities justify learning curve
- • FreeRTOS Tasks: Parallel processing prevents UI blocking during API calls
- • Progressive UI: Visual status indicators address user uncertainty during processing
Critical Technical Challenges
Real-time Audio Processing
Challenge: ESP32 has limited RAM (512KB) for audio buffering
Solution: Implement circular buffer with 4KB chunks, stream directly to API without full file storage
Implementation: Use I2S DMA for hardware-level audio capture, FreeRTOS queue for buffer management
Network Reliability
Challenge: Wi-Fi dropouts during translation cause user frustration
Solution: Exponential backoff retry (1s, 2s, 4s), connection health monitoring, user feedback
Implementation: Background task monitors RSSI, preemptive reconnection, cached translation pairs
Power Management
Challenge: Constant Wi-Fi + display + audio processing drains battery quickly
Solution: Aggressive sleep states, display dimming, Wi-Fi power save mode
Implementation: Modem sleep between translations, 5-second display timeout, 240MHz → 80MHz scaling
Audio Quality Control
Challenge: Background noise and varying input levels affect recognition accuracy
Solution: Software AGC (Automatic Gain Control), noise gate, pre-processing filters
Implementation: Digital filters in ESP32, volume normalisation, silence detection thresholds
Design Pitfalls to Avoid
Complex Menu Systems
Problem: Multi-level menus slow down urgent translation needs
Avoidance: Maximum 2-level menu depth, easy to navigate, clear visual hierarchy
Reference: Travis Touch Go suffers from deep menu navigation
Subscription Dependencies
Problem: Monthly fees create barriers to usage and ownership
Avoidance: Pay-per-use API model, user controls their own API keys, offline fallback
Reference: Pocketalk's $50/year subscription reduces adoption
Fragile Construction
Problem: Travel devices need to survive drops and environmental stress
Avoidance: Reinforced corners, flexible materials, internal shock mounting for electronics
Reference: Many DIY projects fail due to poor mechanical design and circuitry
Unclear Status Indicators
Problem: Users lose confidence when they can't see device state
Avoidance: Always-visible status, progress bars, clear error messages
Reference: Wireless Earbuds (e.g. Samsung Buds 4) provide minimal feedback, causing user confusion
Poor Audio Quality
Problem: Low-quality microphones cause speech recognition failures
Avoidance: Professional-grade I2S microphone, proper acoustic design, noise cancellation
Reference: Arduino projects often use poor analogue microphones
Implementation Strategy Based on Findings
Phase 1: Core Functionality
- • Build minimal hardware (ESP32-S3 + INMP441 + MAX98357A)
- • Implement basic audio capture and playback
- • Test Eleven Labs and LLMs
- • Validate translation pipeline end-to-end
- • Measure latency and audio quality
Phase 2: User Interface
- • Add 2.4" TFT display for visual feedback
- • Implement language selection interface
- • Add status indicators and progress bars
- • Create error handling and retry logic
- • Test usability with target users
Phase 3: Production Ready
- • Design and 3D print professional enclosure
- • Implement power management and battery charging
- • Add fallback API services for reliability
- • Optimise for 3+ second translation targets
- • Conduct durability and field testing
Success Criteria
Success for this project is not just creating a working device, but one that meets specific, measurable targets. This section defines the benchmarks for functionality, performance, usability, and staying within the project constraints. Ensuring this criteria is met will ensure that the device was successful.
1. Functionality
Does the device perform its core tasks correctly?
Core Feature Checklist
- ✓Audio capture starts/stops on command.
- ✓Device connects to Wi-Fi.
- ✓Audio sent to speech-to-text service.
- ✓Text sent to translation service.
- ✓Translated text sent to text-to-speech.
- ✓Translated audio is played.
Accuracy Targets
Translation: >90%
Speech Recognition: >95%
2. Performance & Reliability
How well and how consistently does the device work?
Translation Speed
Target: < 3.0s
Wi-Fi Reconnect
< 15s
Operational Stability
1 Hr
minimum continuous use
3. Usability
Is the device practical and easy for someone to use?
Device Setup
< 60s
to success
Portability
✓
Pocket friendly
Battery Life
1+ Hr
active use
4. Adherence to Constraints
Did the project meet its initial goals and limits?
Final Budget
On Target
$100 maximum
Timeline
On Target
Project started